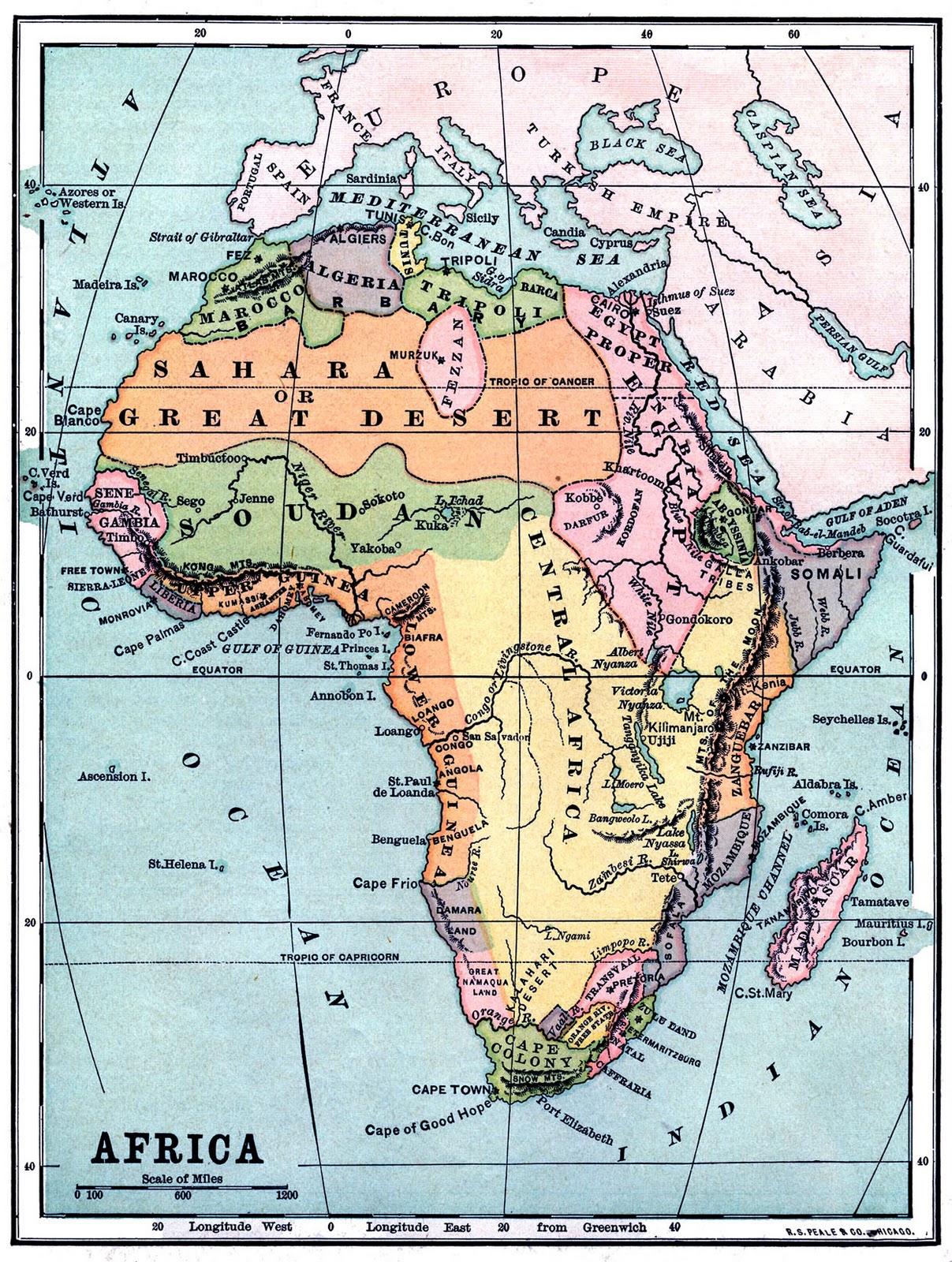
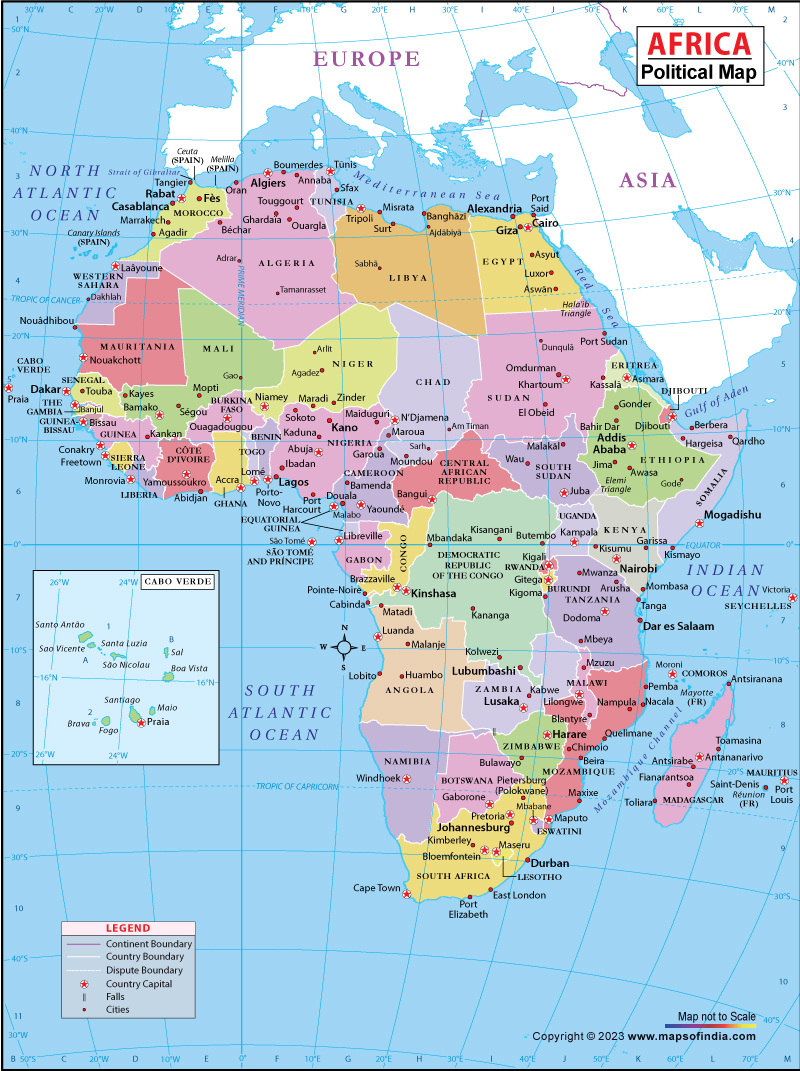
What makes Africa such a fascinating and complex continent? Its sheer diversity in geography, history, culture, and biodiversity sets it apart as one of the most intriguing places on Earth. From the scorching sands of the Sahara to the lush rainforests of the Congo Basin, Africa's landscapes are as varied as its people. This vast continent is home to 54 recognized countries, each with its own unique identity, traditions, and challenges. As we delve deeper into the heart of Africa, we uncover not only its rich heritage but also the pressing issues that shape its modern reality.
Africa stands as the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, encompassing an area of approximately 30.37 million square kilometers. It stretches from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, and from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Indian Ocean in the east. The continent's geography is marked by eight major physical regions, each offering distinct features, flora, and fauna. These include the Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world; the Sahel, a semi-arid transition zone between the Sahara and the savannas; and the Ethiopian Highlands, often referred to as the roof of Africa. Such diversity creates a tapestry of ecosystems that support an extraordinary range of wildlife, making Africa a global biodiversity hotspot.
| Category | Details | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Continent Name | Africa | Britannica |
| Size | Approximately 30.37 million square kilometers | - |
| Population | Over 1.3 billion (estimated) | - |
| Countries | 54 recognized nations | - |
| Major Regions | Sahara, Sahel, Ethiopian Highlands, Congo Basin | - |
| Languages | Thousands of indigenous languages, including Swahili, Hausa, and Amharic | - |
| Religions | Christianity, Islam, traditional African religions | - |
The cultural landscape of Africa is equally diverse, reflecting the continent's long and storied history. Home to some of the earliest human civilizations, Africa has been a cradle of innovation and progress. Ancient Egypt, with its monumental pyramids and sophisticated hieroglyphic writing system, remains one of the most iconic examples of early African achievement. Further south, the Kingdom of Kush thrived along the Nile River, while the Mali Empire became renowned for its wealth and scholarship during the medieval period. Today, this legacy continues through vibrant art, music, literature, and oral traditions that celebrate Africa's rich heritage.
Despite its many strengths, Africa faces significant challenges in the modern era. Economic inequality, political instability, and environmental degradation are among the most pressing issues confronting the continent. Many African nations struggle with poverty, limited access to education and healthcare, and inadequate infrastructure. At the same time, climate change poses a growing threat, exacerbating food insecurity and water scarcity in already vulnerable regions. However, there are reasons for optimism. Across Africa, innovative solutions are being developed to address these challenges, driven by local communities, governments, and international partners working together toward a brighter future.
Language plays a crucial role in shaping African identity and communication. With thousands of indigenous languages spoken across the continent, linguistic diversity is a defining characteristic of Africa. Among the most widely spoken languages are Swahili, Hausa, and Amharic, each serving as a lingua franca in different parts of the continent. In addition to these native tongues, colonial languages such as English, French, Portuguese, and Arabic have become official or co-official languages in many African countries, facilitating cross-cultural exchange and global engagement.
Religion also holds immense significance in African life, influencing everything from daily routines to major celebrations. Christianity and Islam are the dominant faiths, practiced by millions of Africans across the continent. However, traditional African religions continue to thrive alongside these major belief systems, offering unique perspectives on spirituality and community. These religious practices often emphasize harmony with nature, ancestor veneration, and communal responsibility, reinforcing social bonds and fostering resilience in the face of adversity.
As we explore the complexities of Africa, it becomes clear that this remarkable continent defies easy categorization. Its people, cultures, and environments are interconnected yet distinct, creating a dynamic mosaic that evolves over time. Whether examining the historical achievements of ancient empires or addressing contemporary challenges faced by modern societies, Africa offers endless opportunities for discovery and learning. By embracing both its triumphs and struggles, we gain a deeper appreciation for the continent's enduring spirit and potential.
African cities serve as hubs of economic activity, cultural expression, and social interaction. From bustling metropolises like Lagos, Nigeria, and Cairo, Egypt, to smaller urban centers scattered throughout the continent, these areas reflect the rapid pace of urbanization occurring in Africa today. Urban growth presents both opportunities and challenges, as cities strive to balance development with sustainability while ensuring equitable access to resources for all residents. Innovations in technology, architecture, and governance are helping to transform African cities into models of progress and adaptability.
Natural resources form the backbone of many African economies, providing essential raw materials for industries around the globe. The continent is rich in minerals such as gold, diamonds, oil, and natural gas, as well as agricultural products like cocoa, coffee, and tea. However, the extraction and export of these resources often raise concerns about environmental impact, labor conditions, and fair distribution of profits. Efforts to promote sustainable resource management and value-added processing within Africa aim to maximize benefits for local populations while minimizing negative consequences.
Education and healthcare are critical components of Africa's development agenda, requiring sustained investment and collaboration to achieve meaningful improvements. Access to quality education empowers individuals and communities, enabling them to participate fully in societal advancement. Similarly, robust healthcare systems ensure healthier lives and greater productivity, contributing to overall prosperity. Governments, NGOs, and private sector stakeholders are increasingly partnering to enhance educational opportunities and expand healthcare coverage across the continent.
Finally, the importance of preserving Africa's natural and cultural heritage cannot be overstated. National parks, reserves, and protected areas safeguard precious wildlife and habitats, attracting tourists who contribute to conservation efforts and local economies. Meanwhile, museums, festivals, and other cultural institutions celebrate Africa's artistic and intellectual contributions, fostering pride and understanding among citizens and visitors alike. Together, these initiatives help ensure that future generations will inherit a continent rich in beauty, knowledge, and possibility.
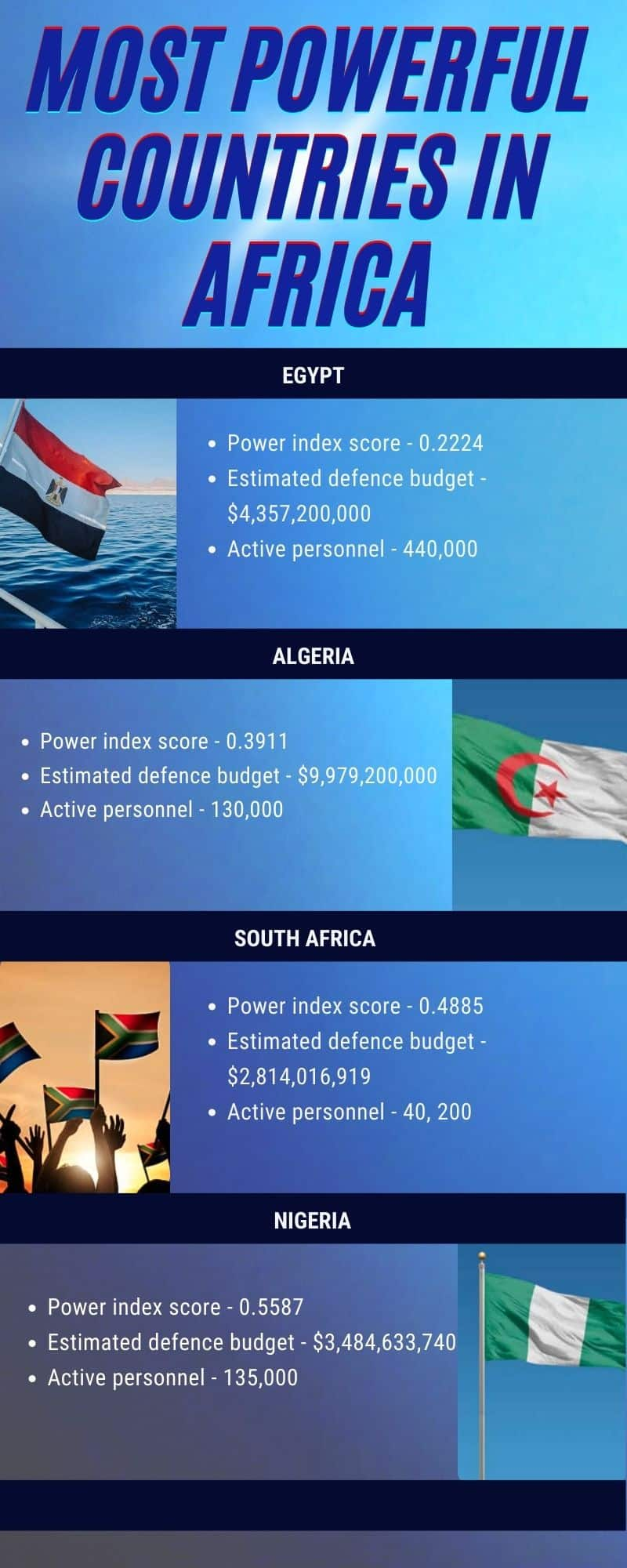
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/map-of-africa-in-1891-showing-routes-of-explorers--artist--unknown--918996998-5b786eb846e0fb0050d5b8e3.jpg)