Is your password one of the weakest ones revealed in 2025? A bold statement from cybersecurity experts warns that millions of users worldwide are at risk due to weak, reused credentials. According to a recent study analyzing over 19 billion exposed passwords, only 6% were unique—a staggering statistic that underscores the widespread crisis of poor password hygiene.
The numbers don't lie: 94% of leaked passwords were reused or duplicated, leaving individuals and organizations vulnerable to credential-stuffing attacks. Despite repeated warnings from security professionals, many users continue to rely on lazy keyboard patterns such as 123456 or overly simplistic combinations like password. These habits expose sensitive information to malicious actors who exploit weak defenses for financial gain or data theft.
| Data Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Name of Study | Cybernews Password Analysis Report |
| Date Range Analyzed | April 2024 - Early 2025 |
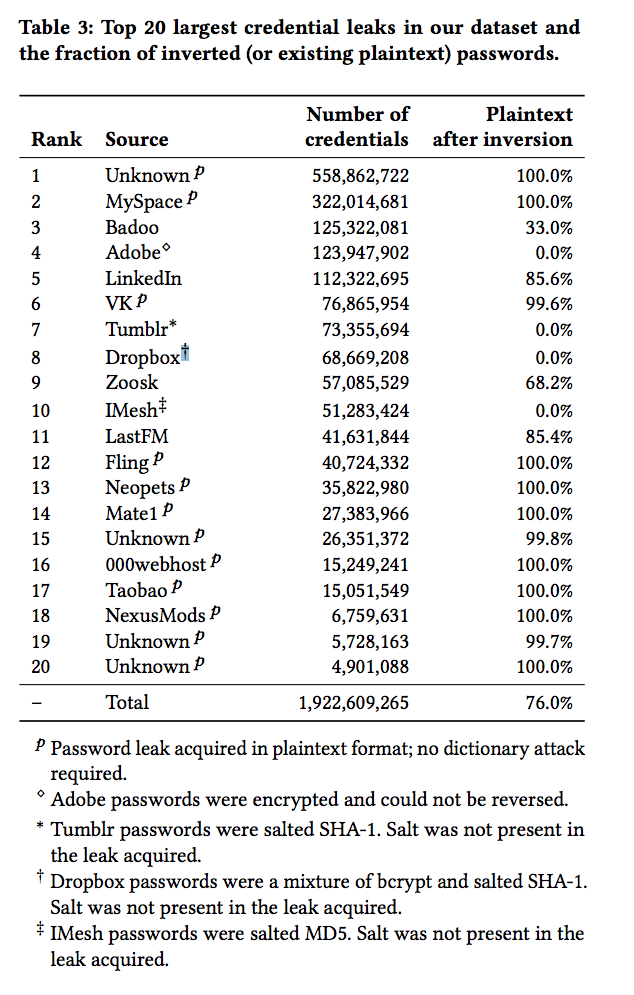
| Total Passwords Analyzed | 19,030,305,929 |
| Unique Password Percentage | 6% |
| Reused/Duplicated Password Percentage | 94% |
| Common Weak Patterns | 123456, password, curse words, food names, brand names, city names |
| Reference Website | Cybernews Official Site |
The implications of this crisis extend far beyond individual accounts. Organizations face significant risks when employees use compromised credentials across multiple platforms. In an era where digital transformation dominates business operations, securing access points has never been more critical. Yet, the data reveals that even corporate environments struggle with enforcing strong authentication practices.
Patterns behind these breaches highlight predictable human behavior. Users frequently opt for convenience over security, choosing easily remembered sequences instead of complex passphrases. This tendency creates fertile ground for attackers employing brute force techniques or leveraging pre-existing databases of stolen credentials. For instance, common phrases such as Ana, popular brand names, or geographic locations often appear among the most frequently breached passwords.
Cybersecurity researchers emphasize that prevention begins with education. Encouraging users to adopt multi-factor authentication (MFA) can significantly reduce vulnerability to unauthorized access. MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring additional verification steps beyond traditional username-password combinations. Furthermore, utilizing password managers helps generate and store complex, unique credentials without burdening memory.
A newly discovered mega-database containing 19 billion compromised passwords has reignited global concern within the cybersecurity community. Believed to have originated from various breaches spanning April 2024 through early 2025, this collection underscores the alarming frequency of large-scale data compromises. Experts warn that without immediate action, the situation will worsen as cybercriminals refine their methods and expand attack surfaces.
Imagine having access to nearly 20 billion passwords—this is precisely what threat actors now possess. With such extensive resources at their disposal, hackers can systematically target high-value accounts using automated tools designed to test billions of combinations against login interfaces. The potential impact ranges from identity theft to corporate espionage, each scenario posing severe consequences for victims.
While technology continues evolving to combat these threats, user behavior remains a persistent weak link. Many people fail to recognize the importance of robust password creation strategies despite increasing awareness campaigns. As demonstrated by the Cybernews study, simple patterns persist despite years of public service announcements urging stronger protections.
To mitigate risks associated with weak passwords, organizations must implement comprehensive policies addressing both technical safeguards and employee training. Regular audits of system permissions ensure outdated credentials do not linger indefinitely. Simultaneously, fostering a culture of vigilance empowers staff members to identify suspicious activities promptly.
For individuals concerned about protecting personal information, several proactive measures exist. Start by reviewing existing accounts and replacing any passwords matching those identified in breach reports. Enable MFA wherever possible, especially for email services, banking portals, and social media platforms. Additionally, consider subscribing to monitoring services alerting you if your data appears in future leaks.
In conclusion, the revelation of 19 billion leaked passwords serves as a stark reminder of ongoing cybersecurity challenges. Addressing this issue requires collective effort from all stakeholders involved—technology providers, businesses, and end-users alike. By prioritizing education, adopting advanced technologies, and promoting best practices, society can work towards reducing vulnerabilities posed by inadequate password management.